파이썬에서 heapq 모듈을 사용하여 최소 힙을 구현할 수 있습니다. 최소 힙을 구현하는 방법의 예는 다음과 같다.
import heapq
class MinHeap:
def __init__(self):
self.heap = []
def push(self, value):
heapq.heappush(self.heap, value)
def pop(self):
return heapq.heappop(self.heap)
def peek(self):
return self.heap[0]
# Example usage:
min_heap = MinHeap()
min_heap.push(5)
min_heap.push(3)
min_heap.push(7)
print(min_heap.pop()) # Output: 3
print(min_heap.peek()) # Output: 5
minheap을 사용하여 Dijkstra 알고리즘을 성공적으로 구현했다. 이제 시간 복잡도를 계산해보자.
이러한 힙 연산의 시간 복잡도는 무엇입니까?
Python 모듈 을 사용한 다양한 힙 연산의 시간 복잡도는 heapq 다음과 같다.
- heapq.heappush: 이 연산의 시간 복잡도는 O(log n)이다. 여기서 n은 힙의 요소 개수다.
- heapq.heappop: 이 연산의 시간 복잡도는 O(log n)이다. 여기서 n은 힙의 요소 개수다.
- 다음을 사용하여 최소 요소에 액세스 heap[0]: 이 작업은 힙의 첫 번째 요소에 직접 액세스 하므로 시간 복잡도가 O(1)이다.
시간 복잡도가 왜 이런 건가요? 내부적으로는 어떻게 작동하나요?
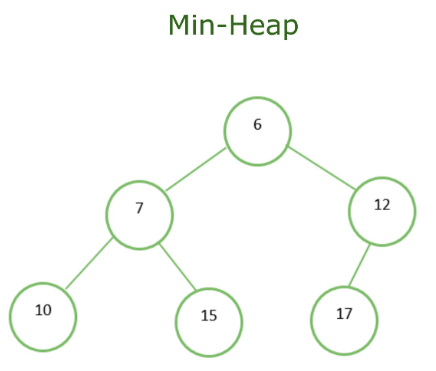
파이썬 모듈 heapq은 힙 속성을 만족하는 데이터 구조인 이진 힙의 구현을 제공한다. 최소 힙에서 주어진 노드 C에 대해 P가 C의 부모 노드이면 P의 키(값)는 C의 키보다 작거나 같다.
이 heapq모듈은 이진 힙의 기본 구현을 활용한다. 이진 힙은 다음 속성을 갖는 이진트리다.
- 완전 이진트리 속성 : 트리의 모든 레벨은 채워져 있지만 마지막 레벨만은 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 채워질 수 있다.
- 힙 순서 속성 : 모든 노드에서 부모 노드의 키는 자식 노드의 키보다 작거나 같고(최소 힙) 자식 노드의 키보다 크거나 같다(최대 힙).
heappush 를 사용하여 요소를 삽입하면 heapq 요소를 목록 끝에 추가한 다음 힙 내에서 요소의 위치를 조정하여 힙 속성을 유지한다. 이 조정에는 힙 순서 속성이 위반되지 않는 한 새로 추가된 요소를 부모 요소와 교체하는 것이 포함된다. 힙 속성을 복원하는 데 필요한 최대 교체 횟수는 힙의 요소 수에 대한 대수적이므로 시간 복잡도는 O(log n)이다.
마찬가지로 heappop 를 사용하여 요소를 제거하면 heapq 루트 요소를 제거하고 힙의 마지막 요소로 대체한 다음 힙 속성을 유지하도록 새 루트 요소의 위치를 조정한다. 이 조정에는 힙 순서 속성이 위반되지 않는 한 새 루트 요소를 가장 작은 자식 요소와 스왑하는 것도 포함된다. 힙 속성을 복원하는 데 필요한 최대 스왑 횟수도 힙의 요소 수에 따라 대수적으로 증가하여 시간 복잡도는 O(log n)이다.
힙의 맨 위에 있는 최소 요소에 직접 접근하는 것(또는 최대 힙의 경우 최대 요소에 접근하는 것)은 단순히 목록의 첫 번째 요소에 접근하기 때문에 상수 시간 연산이다.
이제 데이터 구조에 대한 심층적인 지식을 위해 최소 힙을 처음부터 구현해보자.
heapq 없이 Python에서 최소 힙 구현하기
heapq 모듈을 사용하지 않고도 Python에서 최소 힙을 구현할 수 있다 . 다음은 리스트를 사용한 구현 예다.
class MinHeap:
def __init__(self):
self.heap = []
def push(self, value):
self.heap.append(value)
self._percolate_up(len(self.heap) - 1)
def pop(self):
if not self.heap:
raise IndexError('pop from empty heap')
self._swap(0, len(self.heap) - 1)
min_value = self.heap.pop()
self._percolate_down(0)
return min_value
def peek(self):
if not self.heap:
raise IndexError('peek from empty heap')
return self.heap[0]
def _percolate_up(self, index):
while index > 0:
parent = (index - 1) // 2
if self.heap[index] < self.heap[parent]:
self._swap(index, parent)
index = parent
else:
break
def _percolate_down(self, index):
while index < len(self.heap):
left = 2 * index + 1
right = 2 * index + 2
smallest = index
if left < len(self.heap) and self.heap[left] < self.heap[smallest]:
smallest = left
if right < len(self.heap) and self.heap[right] < self.heap[smallest]:
smallest = right
if smallest != index:
self._swap(index, smallest)
index = smallest
else:
break
def _swap(self, i, j):
self.heap[i], self.heap[j] = self.heap[j], self.heap[i]
# Example usage:
min_heap = MinHeap()
min_heap.push(5)
min_heap.push(3)
min_heap.push(7)
print(min_heap.pop()) # Output: 3
print(min_heap.peek()) # Output: 5
이 코드에서 push, pop, peek 연산은 클래스의 메서드로 구현되고 MinHeap, 및 _percolate_up메서드 _percolate_down는 삽입 및 삭제 중에 힙 속성이 유지되도록 보장한다.
원문 : https://code.likeagirl.io/python-min-heap-priority-queue-interview-prep-66f127db1176
'development > python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Flask vs FastAPI 비교 분석 (4) | 2024.11.06 |
|---|